Learning Outcomes
i. Students will explore various examples of how Pascal's law is applied in real-world scenarios.
ii. Examine the working mechanisms of hydraulic brakes, hydraulic lifts, and hydraulic presses, understanding how Pascal's law allows for the transmission of force over long distances.
iii. Comprehend the concept of force multiplication in hydraulic systems, realizing how small forces can produce large effects.
iv. Appreciate the versatility of Pascal's law and its widespread use in various industries and applications.
v. Recognize the role of Pascal's law in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of mechanical systems.
Introduction
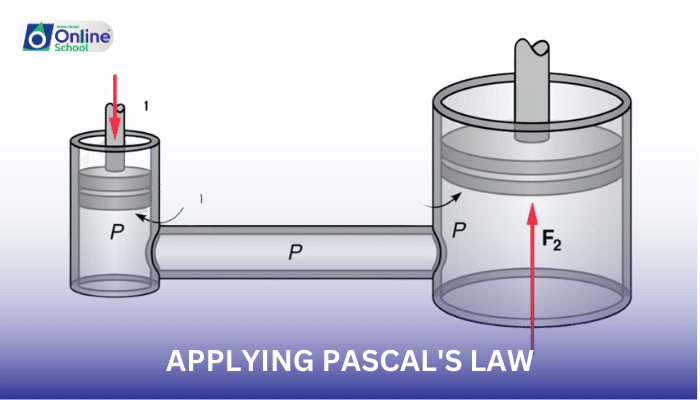
Blaise Pascal's law, a fundamental principle in fluid mechanics, has transformed the way we harness force and power. Its essence lies in the equal distribution of pressure within an enclosed fluid, enabling the transmission of force without loss. This remarkable property has revolutionized engineering, leading to the development of innovative hydraulic systems that play a pivotal role in our modern world.
i. Hydraulic Brakes: A Force-Multiplying Masterpiece
Hydraulic brakes, ubiquitous in automobiles, exemplify the practical application of Pascal's law. When the driver presses the brake pedal, a small force is applied to a piston in a confined fluid. Pascal's law ensures that this pressure is transmitted equally throughout the system, reaching the brake pads that press against the wheels. The result is a significant amplification of force, enabling the driver to control the vehicle's speed effectively.
ii. Hydraulic Lifts: Elevating Heavy Loads with Ease
Hydraulic lifts, commonly used in car workshops, rely on Pascal's law to raise and lower heavy vehicles with minimal effort. A small force applied to a hydraulic piston in a reservoir of fluid is transmitted to a larger piston connected to the platform supporting the vehicle. This force amplification allows the lift to raise heavy loads with relative ease.
iii. Hydraulic Presses: Shaping Materials with Powerful Force
Hydraulic presses, found in various industries, employ Pascal's law to generate immense forces for compressing, shaping, or embossing materials. A small force applied to a hydraulic piston is amplified through Pascal's law, resulting in a large force being exerted on the press ram. This allows for the precise and powerful manipulation of materials.
iv. Force Multiplication: A Hydraulic Advantage
The amplification of force in hydraulic systems is known as the hydraulic advantage. This advantage is calculated as the ratio of the output force to the input force. By carefully choosing piston sizes, engineers can design hydraulic systems with high hydraulic advantages, enabling large forces to be generated from small applied forces.
v. A Versatile Principle: Beyond Hydraulics
Pascal's law extends beyond hydraulic systems, finding applications in various fields:
Medicine: Syringes and IV drips rely on Pascal's law to deliver fluids precisely.
Construction: Hydraulic pumps and power tools utilize Pascal's law to generate high forces for lifting and moving objects.
Aviation: Hydraulic systems in aircraft control flight surfaces and landing gear.
Pascal's law, a cornerstone of fluid mechanics, has revolutionized engineering and permeated various industries. Its ability to transmit force efficiently and amplify power has led to the development of innovative hydraulic systems that make our lives easier and safer. As we witness the widespread application of Pascal's law, we appreciate its versatility and profound impact on our modern world.